CorrCAD/CorrCAD Plus
CorrCAD tackles a large variety of practical scientific and engineering corrosion problems, both onshore and offshore, realistically and accurately. CorrCAD can predict the degree of corrosion control provided by a system such as ICCP (Impressed Current Corrosion Protection) or GACP / SACP (Galvanic/Sacrificial Anode Corrosion Protection). It can also evaluate the effect of stray currents such as those produced by HVDC electrodes or dc rail traction systems on the corrosion of buried metallic structures. CorrCAD provides state-of-the-art methods to help optimize the location and characteristics of the corrosion protective system and minimize stray current interference effects on protected structures such as onshore pipelines and tanks, offshore oil platforms, marine loading docks, and other similar facilities.
Applicable Software Computation ModulesTechnical Description
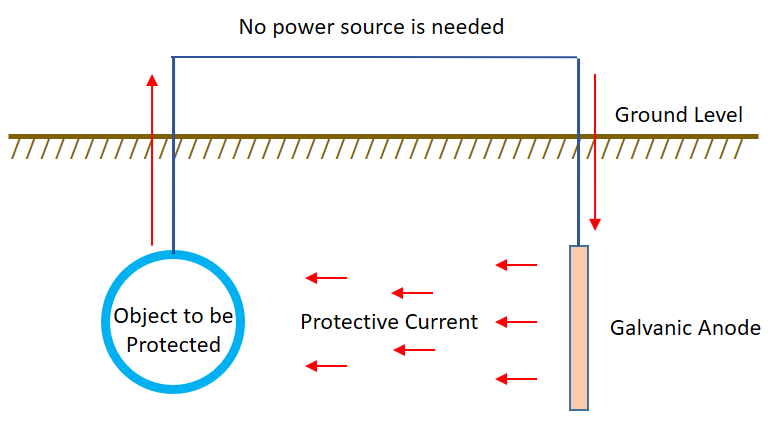
CorrCAD’s main function is to determine the degree of corrosion control provided by a system. Typical applications of CorrCAD for corrosion control include Impressed Cathodic Current Protection systems (ICCP) where a cathodic current is injected in the structure to be protected, and the connection of more electrochemically active metals to the one being protected (i.e., a more anodic material) in Sacrificial or Galvanic Anode Cathodic Protection systems (GACP or SACP) where the anode provides electrons to replace those which are lost during oxidation of the protected metal.
Another application of CorrCAD is to estimate the effect of stray currents such as those produced by HVDC electrodes or DC rail traction systems on the corrosion of buried metallic structures. It can evaluate the corrosion status of the structure and help optimize the location and characteristics of the corrosion protective system (such as ICCP or GACP) to minimize stray current interference effects on protected structures such as pipelines, tanks, oil platform, ships, and marine loading docks, and other similar facilities.
Technical Highlights
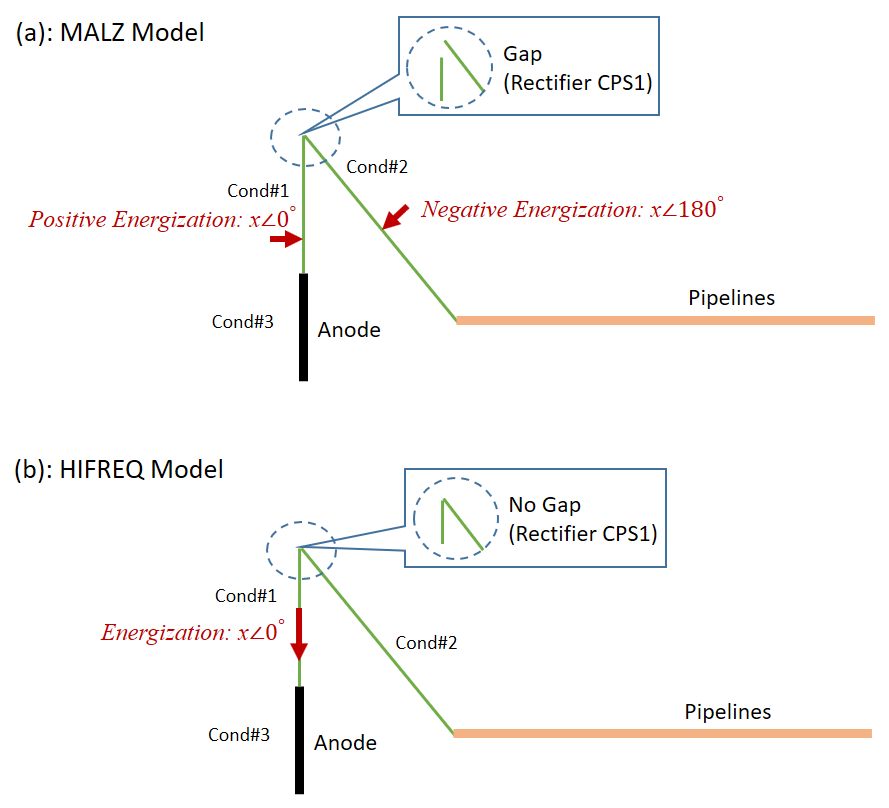
The CAD-based graphical user interface offers a complete and simple solution for defining complex networks accurately, displaying and editing the protected structures and their protection systems, and for computing and examining the results. CorrCAD integrates the computational power of the MALZ and HIFREQ modules, including its capability to calculate conductor currents of large conductor networks, and the resolution of non-linear electrochemical boundary conditions, using a fixed-point iteration approach. The MALZ and HIFREQ computation modules are the main engines that calculate conductor currents and electromagnetic fields in an arbitrary network immersed in arbitrary soil structures. The resolution of CP problems uses the numerical methods of MALZ or HIFREQ with the simple fixed-point iteration. It starts with an initial value of potential or current, and solves the non-linear boundary conditions. The polarization curve (non-linear boundary condition) is used during the iterative process to compute the new entry (potential or current) for the next iteration. The iteration is stopped when the difference of two successive steps is smaller than a specified tolerance threshold, or when a maximum number of iterations is reached.
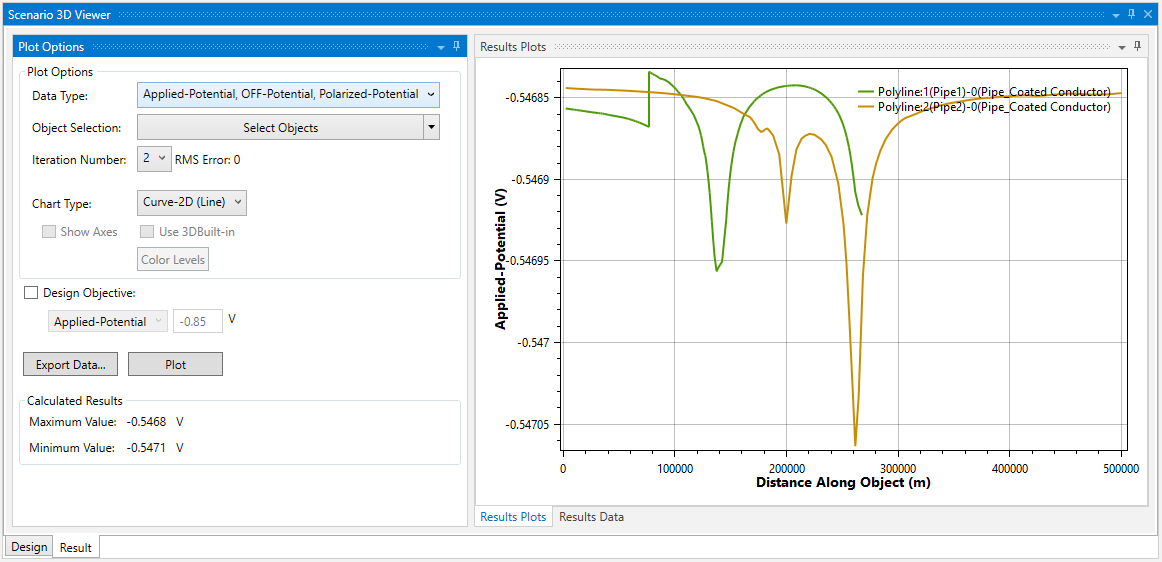
The CorrCAD computation modules consider polarization effects, i.e., they do consider the polarization resistance. The computed structure-to-soil potential is the potential difference between the protected structure metal potential and electrolyte potential at the reference point, and it includes the polarization potential. The potential drop across the coating and the soil potential drop to remote soil, i.e., the “ON” reading, are both considered as IR drop that should be eliminated from the cathodic protection effectiveness evaluation. The real effectiveness measure of the CP or direct characterization of stray current interference level is the polarization potential, i.e., the “OFF” reading. That being said, CorrCAD:
CorrCAD offers the possibility of determining the corrosion effectiveness considering experimental polarization data such as polarization curves. When there is a good coating on the pipe, CorrCAD computes the current density by using the provided coated steel polarization curve, then eliminates the effects of IR drops, so that the coating protection current density and corresponding over-potential (responding to the “OFF” reading) are accurately obtained.
CorrCAD Capabilities
The following summarizes the capabilities of the CorrCAD software package.
Intuitive Interface and Powerful Functionalities
CorrCAD provides a highly intuitive graphical user interface that simplifies and reduce the time needed to specify the parameters of the system to be analyzed. The main features and functionalities of this interface are:
The Desktop CAD Interface
This interface allows you to import or define metallic structure path coordinates in graphical or tabular form using various standard formats, such as Excel CSV, MALT, MALZ or HIFREQ SES SICL files and Google Earth™ KML files. Appropriate characteristics with different Cross-Sections can be assigned to each path.
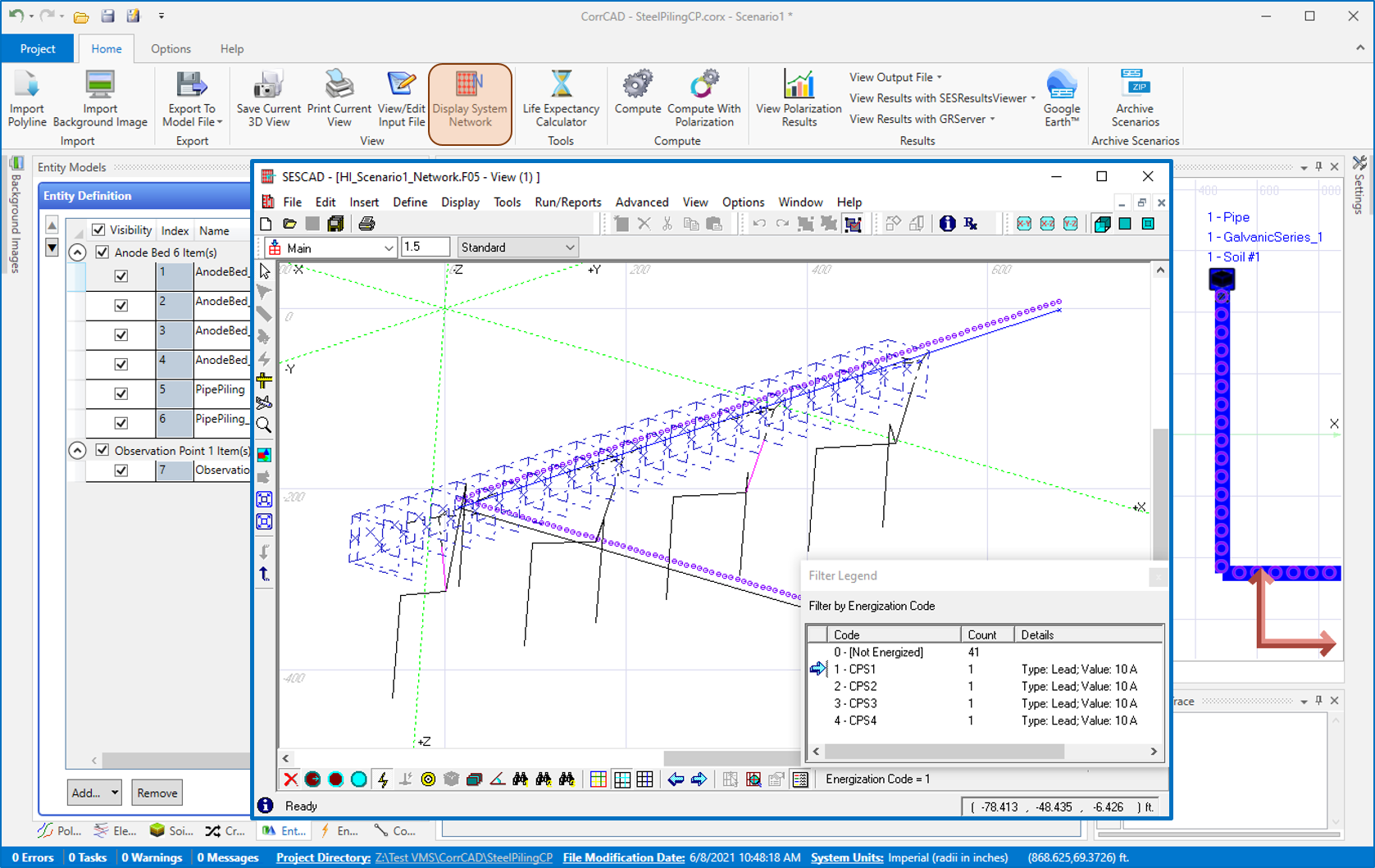
Multiple Energizations
Appropriate energization of a network of metallic structures is essential when performing corrosion protection studies. CorrCAD provides the ability to energize the system at defined intervals or arbitrary locations. This capability provides an easy way to compute pipe-to-soil potentials (this simulates the CP “ON” readings in the field) along pipelines and similar structures and to verify that pipe-to-soil potentials do not attenuate to inadequate levels far from the rectifiers and that pipe-to-soil potentials are not excessive at current feed locations (i.e., rectifiers).
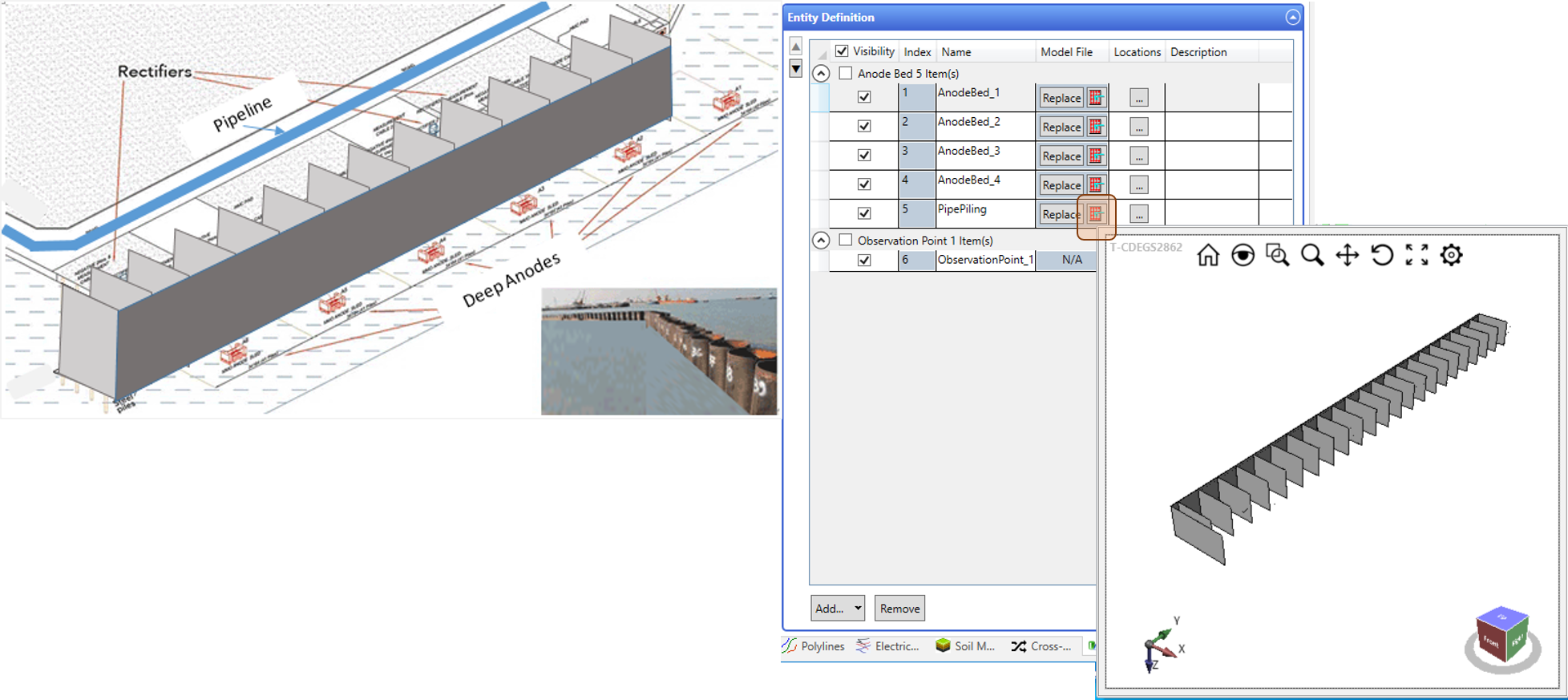
Anode and any Customized Entity Structure models
CorrCAD supports detailed modeling for anodes, cables, plates or any structure using the Entity modeling feature, which can be pre-defined in a MALZ or HIFREQ file and imported from the provided library database collections, and can then be inserted at any location in the system network.
Anode Performance and Complex Soils
CorrCAD provides detailed information on the performance of individual sacrificial anodes, such as the anode consumption rate, life expectancy and remaining life. Furthermore, an analysis of anode beds is available. All analyses can be carried out for multi-layered and arbitrary soil models. A soil model can be easily imported from a RESAP output file or from a SoilModelEditor file, a MALZ or HIFREQ input file or it can simply be defined in the embedded SoilModelEditor module.
Native Potential vs Copper Sulfate Electrode or Standard Hydrogen Electrode
Native (Galvanic Series) potentials can be specified in CorrCAD to account for a metal’s natural potential with respect to soil. In the present version, values measured with respect to Copper Sulfate Electrodes (CSE) and Standard Hydrogen Electrodes (SHE) can be imported for convenience. Polarization effects representing the behavior of both metallic structures and anodes are considered, if applicable.
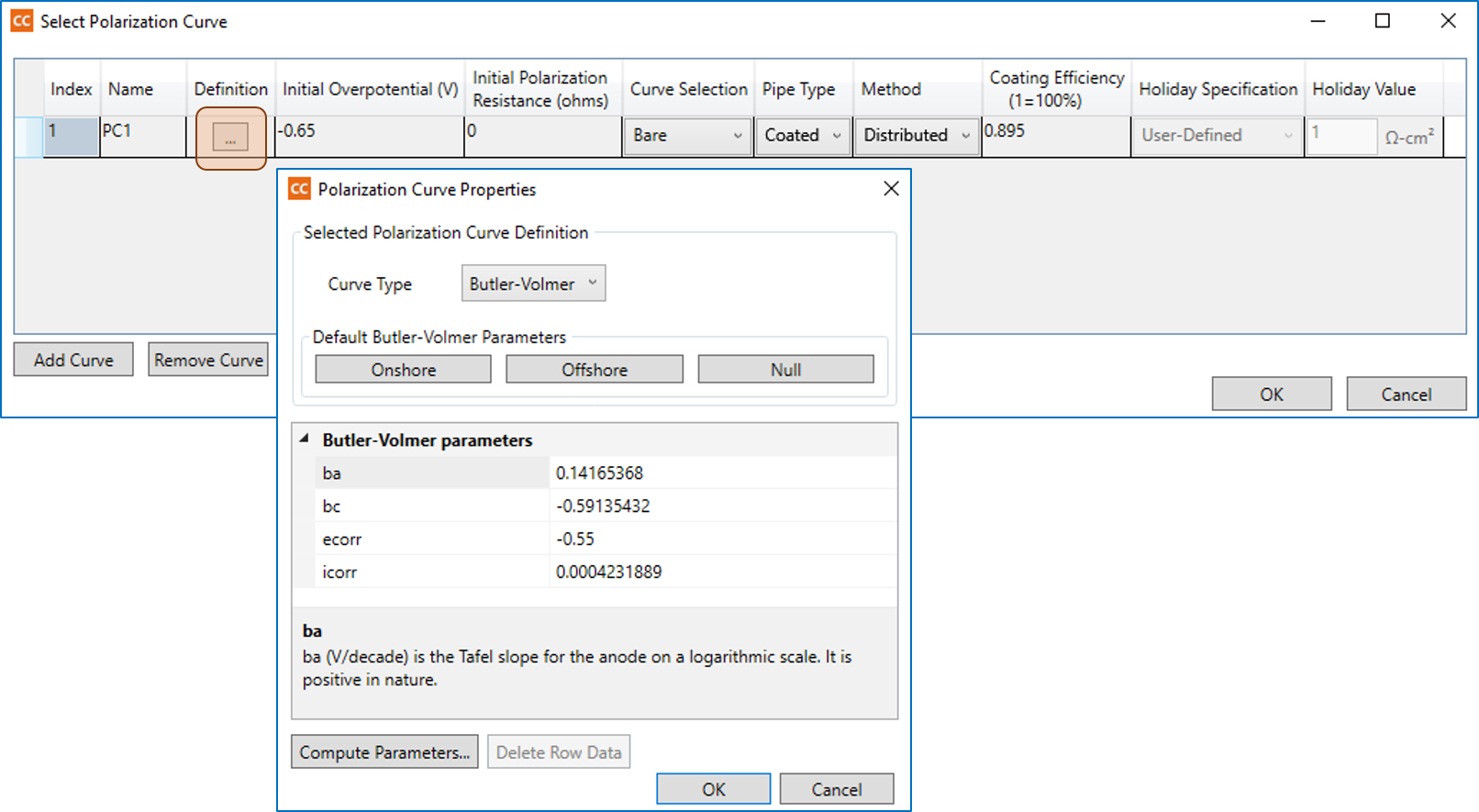
Polarization
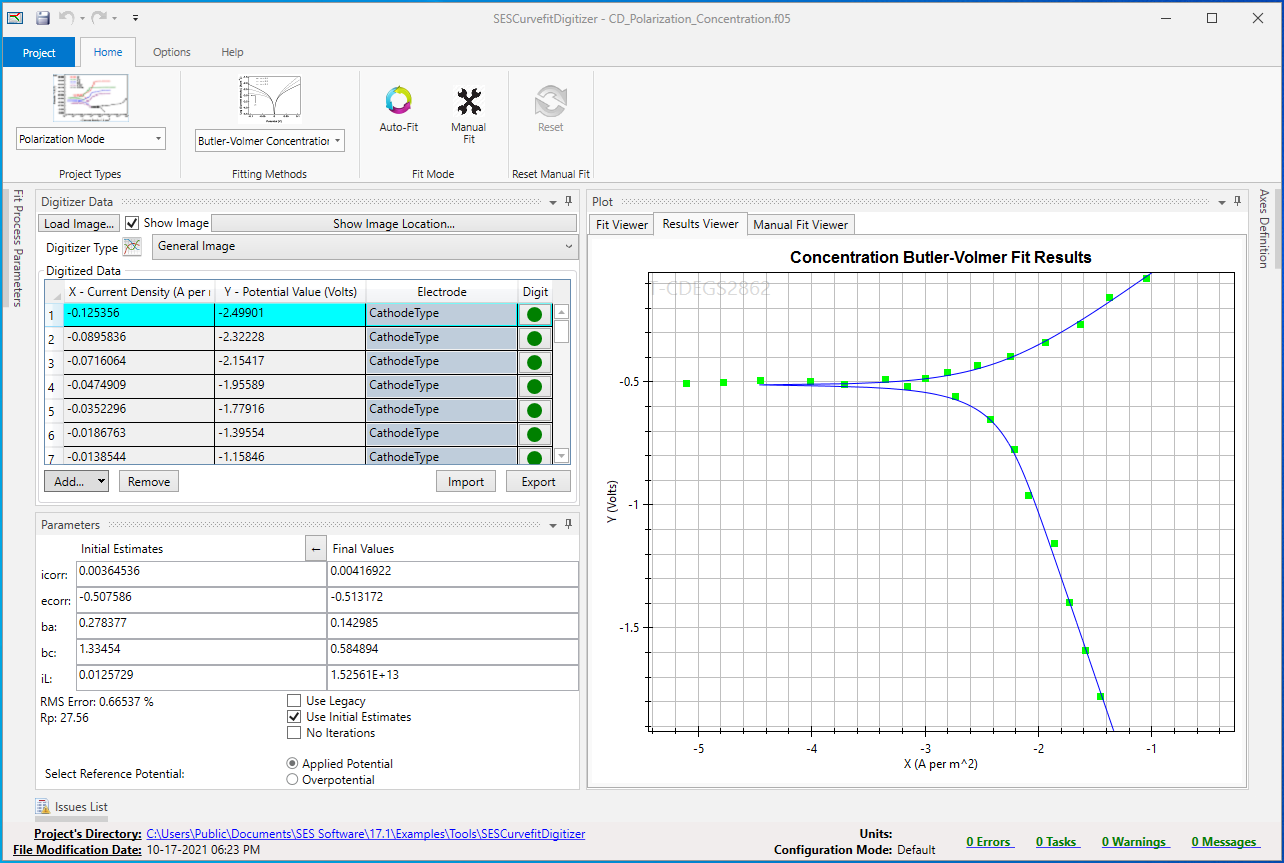
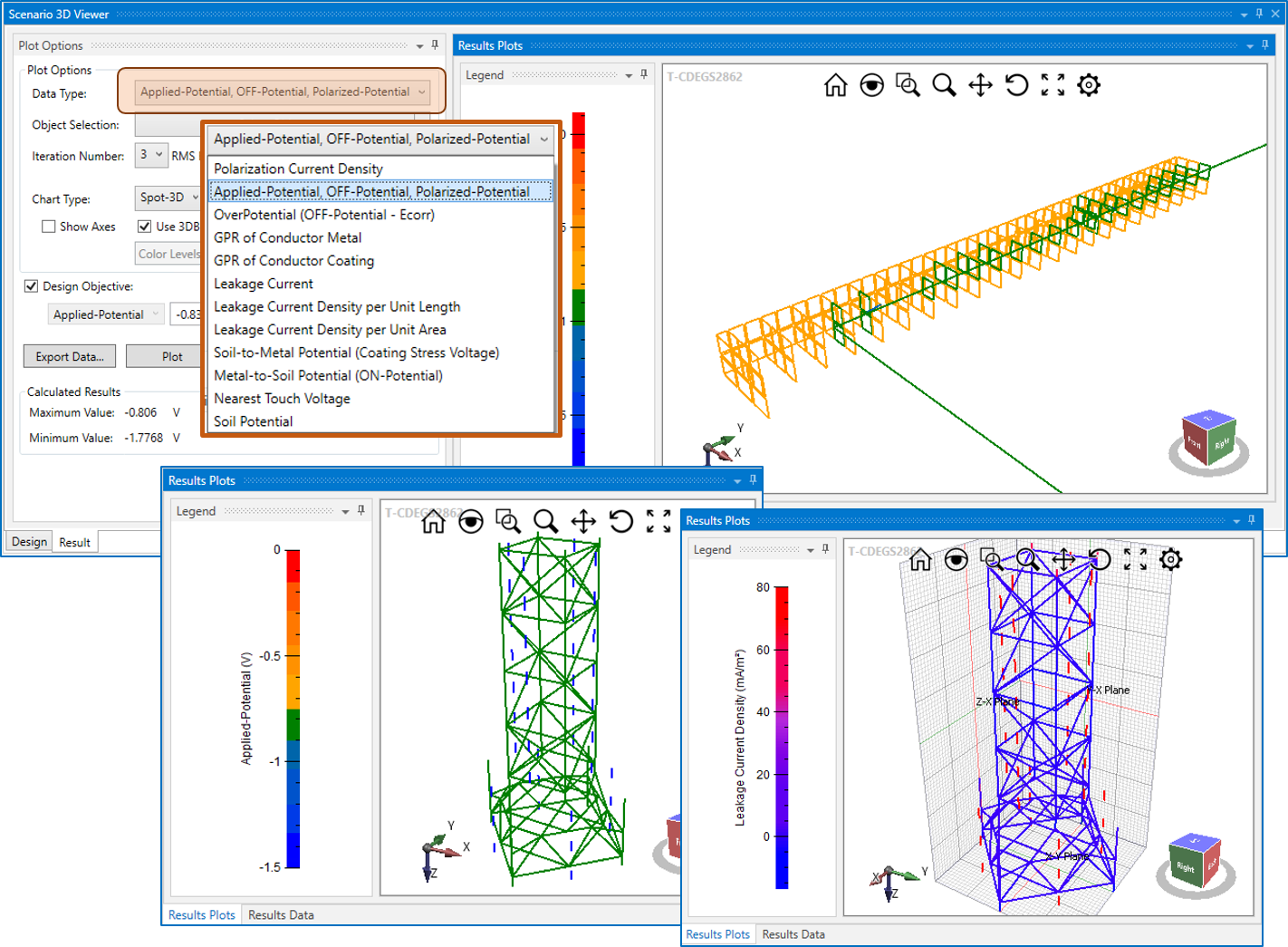
Polarization curves for each individual electrochemical reaction, cathodic and anodic reactions and polarization can optionally be specified and displayed and will be used in the computations. CorrCAD provides a digitization tool, named SESCurveFitDigitizer, which can digitize polarization curves in standard image formats in order to obtain the polarization curve parameters needed to perform a complete corrosion analysis according to the type of function selected.
Comprehensive Outputs and Display Tools
The relevant computed values can be displayed in 2D curve, 2D-Spot or 3D plot. Most of the results can be exported to an Excel CSV file format.
Context Sensitive On-line Help
When you need an explanation or a rapid reminder of what any portion of a screen is for, simply click on that part of the screen, press the F1 key, and a context-sensitive help screen pops up instantly.
CorrCAD Plus
CorrCAD Plus expands the CorrCAD package capabilities to carry out grounding/earthing analysis at all frequencies, not only DC. The MALZ module in CorrCAD Plus has the ability to analyze buried metallic networks in the frequency domain.